Working principle of crystal resonator
What is quartz
The chemical composition of quartz is SiO2. The crystal belongs to the oxide mineral of hexagonal system, that is, low-temperature quartz (a-quartz), which is the most widely distributed mineral species in quartz family minerals. In a broad sense, quartz also includes high-temperature quartz (b-quartz). Piezoelectric effect can be produced when subjected to pressure or heat.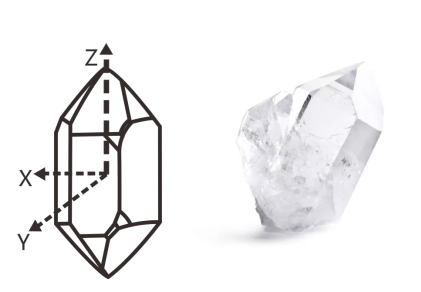
Quartz crystal oscillator is a resonant device made by using the piezoelectric effect of quartz crystal. Its basic structure is roughly as follows: a thin slice is cut from a quartz crystal at a certain azimuth angle (the commonly used wafer cut type is divided into two types: AT cut and BT cut), silver is plated on its two corresponding surfaces as electrodes, a lead is welded on each electrode to connect to the pin, and then a packaging shell is added to form a quartz crystal resonator, referred to as quartz crystal or crystal, crystal oscillator. Its products are generally packaged in metal shells, and some are packaged in glass shells, ceramics or plastics.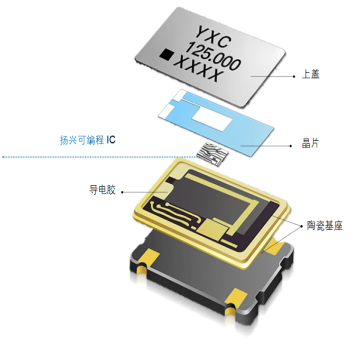
Piezoelectric effect: If an electric field is applied to the two electrodes of a quartz crystal, the wafer will produce mechanical deformation. On the contrary, if mechanical pressure is applied to both sides of the chip, an electric field will be generated in the corresponding direction of the chip. This physical phenomenon is called piezoelectric effect.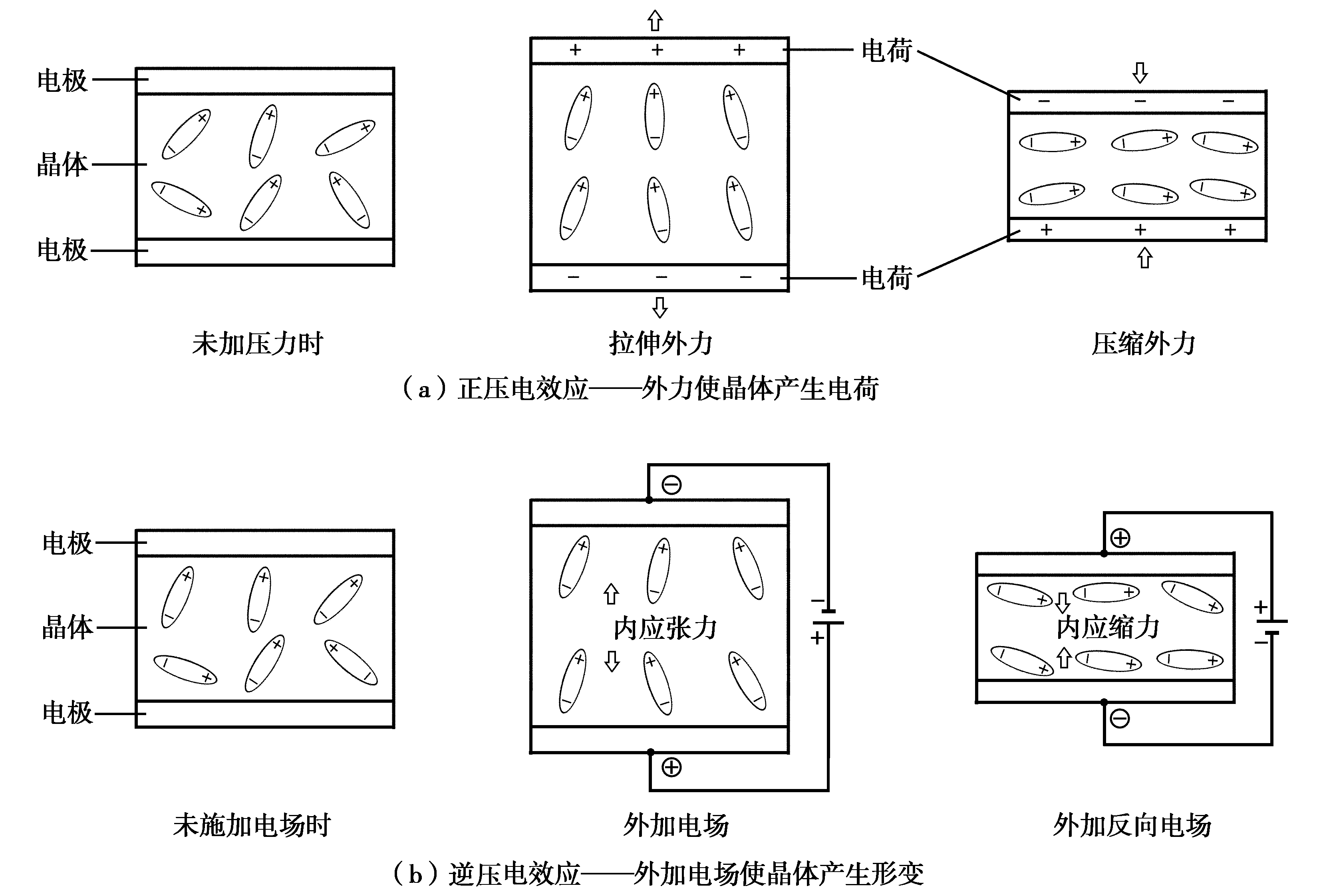
If an alternating voltage is applied to the two poles of the chip, the chip will generate mechanical vibration, and the mechanical vibration of the chip will generate an alternating electric field.
Under normal circumstances, the amplitude of the mechanical vibration of the chip and the amplitude of the alternating electric field are very small, but when the frequency of the applied alternating voltage is a certain value, the amplitude is significantly increased, much larger than the amplitude at other frequencies. This phenomenon is called piezoelectric resonance, which is very similar to the resonance phenomenon of the LC circuit. Its resonant frequency is related to the cutting method, geometry, size, etc. of the chip.
When the crystal does not vibrate, it can be regarded as a flat plate capacitor called electrostatic capacitance C. Its size is related to the geometric size of the chip and the electrode area, generally about a few picofarads to tens of picofarads. When the crystal oscillates, the inertia of the mechanical vibration can be equivalent to the inductance L.